 |
| September 19, 2023 | Volume 19 Issue 35 |
Motion Control News & Products
Designfax weekly eMagazine
Archives
Partners
Manufacturing Center
Product Spotlight
Modern Applications News
Metalworking Ideas For
Today's Job Shops
Tooling and Production
Strategies for large
metalworking plants
Linear guide system corrects misalignments
 Bishop-Wisecarver's UtiliTrak® linear guide system includes vee rails for precision and open rails for misalignment float to provide smooth and accurate motion on inaccurate structures. Because precise parallelism is difficult to achieve, it is not uncommon for mounting surfaces to be slightly out of parallel. UtiliTrak's design compensates for mounting errors and does not require absolute parallelism for accurate operation. Genius.
Bishop-Wisecarver's UtiliTrak® linear guide system includes vee rails for precision and open rails for misalignment float to provide smooth and accurate motion on inaccurate structures. Because precise parallelism is difficult to achieve, it is not uncommon for mounting surfaces to be slightly out of parallel. UtiliTrak's design compensates for mounting errors and does not require absolute parallelism for accurate operation. Genius.
Learn more.
Universal Robots emerges as preferred robotics platform for AI solutions at Automate 2024
 At North America's largest automation show (Chicago, May 6-9), cobot pioneer Universal Robots will redefine the frontiers of physical AI, showcasing how the "ChatGPT moment for robots" has arrived in a wide range of applications. Automate attendees will also experience how Universal Robots' newest cobot models, the UR20 and UR30, automate tasks with increased payload, reach, and torque.
At North America's largest automation show (Chicago, May 6-9), cobot pioneer Universal Robots will redefine the frontiers of physical AI, showcasing how the "ChatGPT moment for robots" has arrived in a wide range of applications. Automate attendees will also experience how Universal Robots' newest cobot models, the UR20 and UR30, automate tasks with increased payload, reach, and torque.
Learn more.
Multi-stage mini vacuum pumps: Max performance
 Designed to meet the demanding needs of industrial users, the CMS M series mini vacuum pump from COVAL combines robustness, performance, and modularity, offering an optimum solution for applications requiring high suction flow rates, such as gripping porous parts, emptying tanks, or material handling when integrated into vacuum grippers. Thanks to their ultra-compact design and optimized multi-stage Venturi system, these pumps guarantee powerful suction flows up to 19.42 SCFM, while reducing compressed air consumption in a compact footprint.
Designed to meet the demanding needs of industrial users, the CMS M series mini vacuum pump from COVAL combines robustness, performance, and modularity, offering an optimum solution for applications requiring high suction flow rates, such as gripping porous parts, emptying tanks, or material handling when integrated into vacuum grippers. Thanks to their ultra-compact design and optimized multi-stage Venturi system, these pumps guarantee powerful suction flows up to 19.42 SCFM, while reducing compressed air consumption in a compact footprint.
Learn more.
Choosing a stepper motor: PM or hybrid?
 Lin Engineering stepper motors are widely used in various applications that require precise control of motion, such as in robotics, 3D printing, CNC machines, and medical equipment. There are two main types of stepper motors: permanent magnet (PM) and hybrid. Learn the differences, advantages, and when to use one type or the other.
Lin Engineering stepper motors are widely used in various applications that require precise control of motion, such as in robotics, 3D printing, CNC machines, and medical equipment. There are two main types of stepper motors: permanent magnet (PM) and hybrid. Learn the differences, advantages, and when to use one type or the other.
Read this informative Lin Engineering article.
Top Product: Integrated servo system is 20% smaller than standalone unit
 Applied Motion Products has introduced the MDX+ series, a family of low-voltage servo systems that integrate a servo drive, motor, and encoder into one package. This all-in-one drive unit is an ideal solution for manufacturers in logistics, AGV, medical, semiconductor, the solar industries, and many others.
Applied Motion Products has introduced the MDX+ series, a family of low-voltage servo systems that integrate a servo drive, motor, and encoder into one package. This all-in-one drive unit is an ideal solution for manufacturers in logistics, AGV, medical, semiconductor, the solar industries, and many others.
Read the full article.
Overhung load adaptors provide load support and contamination protection
 Overhung load adaptors (OHLA) provide both overhung radial and axial load support to protect electrified mobile equipment motors from heavy application loads, extending the lifetime of the motor and alleviating the cost of downtime both from maintenance costs and loss of production. They seal out dirt, grime, and other contaminants too. Zero-Max OHLAs are available in an extensive offering of standard models (including Extra-Duty options) for typical applications or customized designs.
Overhung load adaptors (OHLA) provide both overhung radial and axial load support to protect electrified mobile equipment motors from heavy application loads, extending the lifetime of the motor and alleviating the cost of downtime both from maintenance costs and loss of production. They seal out dirt, grime, and other contaminants too. Zero-Max OHLAs are available in an extensive offering of standard models (including Extra-Duty options) for typical applications or customized designs.
Learn more.
Why choose electric for linear actuators?
 Tolomatic has been delivering a new type of linear motion technology that is giving hydraulics a run for its money. Learn the benefits of electric linear motion systems, the iceberg principle showing total cost of ownership, critical parameters of sizing, and conversion tips.
Tolomatic has been delivering a new type of linear motion technology that is giving hydraulics a run for its money. Learn the benefits of electric linear motion systems, the iceberg principle showing total cost of ownership, critical parameters of sizing, and conversion tips.
Get this informative e-book. (No registration required)
New AC hypoid inverter-duty gearmotors
 Bodine Electric Company introduces 12 new AC inverter-duty hypoid hollow shaft gearmotors. These type 42R-25H2 and 42R-30H3 drives combine an all-new AC inverter-duty, 230/460-VAC motor with two hypoid gearheads. When used with an AC inverter (VFD) control, these units deliver maintenance-free and reliable high-torque output. They are ideal for conveyors, gates, packaging, and other industrial automation equipment that demands both high torque and low power consumption from the driving gearmotor.
Bodine Electric Company introduces 12 new AC inverter-duty hypoid hollow shaft gearmotors. These type 42R-25H2 and 42R-30H3 drives combine an all-new AC inverter-duty, 230/460-VAC motor with two hypoid gearheads. When used with an AC inverter (VFD) control, these units deliver maintenance-free and reliable high-torque output. They are ideal for conveyors, gates, packaging, and other industrial automation equipment that demands both high torque and low power consumption from the driving gearmotor.
Learn more.
Next-gen warehouse automation: Siemens, Universal Robots, and Zivid partner up
 Universal Robots, Siemens, and Zivid have created a new solution combining UR's cobot arms with Siemens' SIMATIC Robot Pick AI software and Zivid's 3D sensors to create a deep-learning picking solution for warehouse automation and intra-logistics fulfillment. It works regardless of object shape, size, opacity, or transparency and is a significant leap in solving the complex challenges faced by the logistics and e-commerce sectors.
Universal Robots, Siemens, and Zivid have created a new solution combining UR's cobot arms with Siemens' SIMATIC Robot Pick AI software and Zivid's 3D sensors to create a deep-learning picking solution for warehouse automation and intra-logistics fulfillment. It works regardless of object shape, size, opacity, or transparency and is a significant leap in solving the complex challenges faced by the logistics and e-commerce sectors.
Read the full article.
Innovative DuoDrive gear and motor unit is UL/CSA certified
 The DuoDrive integrated gear unit and motor from NORD DRIVE-SYSTEMS is a compact, high-efficiency
solution engineered for users in the fields of intralogistics, pharmaceutical, and the food and beverage industries. This drive combines a IE5+ synchronous motor and single-stage helical gear unit into one compact housing with a smooth, easy-to-clean surface. It has a system efficiency up to 92% and is available in two case sizes with a power range of 0.5 to 4.0 hp.
The DuoDrive integrated gear unit and motor from NORD DRIVE-SYSTEMS is a compact, high-efficiency
solution engineered for users in the fields of intralogistics, pharmaceutical, and the food and beverage industries. This drive combines a IE5+ synchronous motor and single-stage helical gear unit into one compact housing with a smooth, easy-to-clean surface. It has a system efficiency up to 92% and is available in two case sizes with a power range of 0.5 to 4.0 hp.
Learn more.
BLDC flat motor with high output torque and speed reduction
 Portescap's 60ECF brushless DC slotted flat motor is the newest frame size to join its flat motor portfolio. This 60-mm BLDC motor features a 38.2-mm body length and an outer-rotor slotted configuration with an open-body design, allowing it to deliver improved heat management in a compact package. Combined with Portescap gearheads, it delivers extremely high output torque and speed reduction. Available in both sensored and sensorless options. A great choice for applications such as electric grippers and exoskeletons, eVTOLs, and surgical robots.
Portescap's 60ECF brushless DC slotted flat motor is the newest frame size to join its flat motor portfolio. This 60-mm BLDC motor features a 38.2-mm body length and an outer-rotor slotted configuration with an open-body design, allowing it to deliver improved heat management in a compact package. Combined with Portescap gearheads, it delivers extremely high output torque and speed reduction. Available in both sensored and sensorless options. A great choice for applications such as electric grippers and exoskeletons, eVTOLs, and surgical robots.
Learn more and view all the specs.
Application story: Complete gearbox and coupling assembly for actuator system
 Learn how GAM engineers not only sized and selected the appropriate gear reducers and couplings required to drive two ball screws in unison using a single motor, but how they also designed the mounting adapters necessary to complete the system. One-stop shopping eliminated unnecessary components and resulted in a 15% reduction in system cost.
Learn how GAM engineers not only sized and selected the appropriate gear reducers and couplings required to drive two ball screws in unison using a single motor, but how they also designed the mounting adapters necessary to complete the system. One-stop shopping eliminated unnecessary components and resulted in a 15% reduction in system cost.
Read this informative GAM blog.
Next-gen motor for pump and fan applications
 The next evolution of the award-winning Aircore EC motor from Infinitum is a high-efficiency system designed to power commercial and industrial applications such as HVAC fans, pumps, and data centers with less energy consumption, reduced emissions, and reduced waste. It features an integrated variable frequency drive and delivers upward of 93% system efficiency, as well as class-leading power and torque density in a low-footprint package that is 20% lighter than the previous version. Four sizes available.
The next evolution of the award-winning Aircore EC motor from Infinitum is a high-efficiency system designed to power commercial and industrial applications such as HVAC fans, pumps, and data centers with less energy consumption, reduced emissions, and reduced waste. It features an integrated variable frequency drive and delivers upward of 93% system efficiency, as well as class-leading power and torque density in a low-footprint package that is 20% lighter than the previous version. Four sizes available.
Learn more.
Telescoping linear actuators for space-constrained applications
 Rollon's new TLS telescoping linear actuators enable long stroke lengths with minimal closed lengths, which is especially good for applications with minimal vertical clearance. These actuators integrate seamlessly into multi-axis systems and are available in two- or three-stage versions. Equipped with a built-in automated lubrication system, the TLS Series features a synchronized drive system, requiring only a single motor to achieve motion. Four sizes (100, 230, 280, and 360) with up to 3,000-mm stroke length.
Rollon's new TLS telescoping linear actuators enable long stroke lengths with minimal closed lengths, which is especially good for applications with minimal vertical clearance. These actuators integrate seamlessly into multi-axis systems and are available in two- or three-stage versions. Equipped with a built-in automated lubrication system, the TLS Series features a synchronized drive system, requiring only a single motor to achieve motion. Four sizes (100, 230, 280, and 360) with up to 3,000-mm stroke length.
Learn more.
Competitively priced long-stroke parallel gripper
 The DHPL from Festo is a new generation of pneumatic long-stroke grippers that offers a host of advantages for high-load and high-torque applications. It is interchangeable with competitive long-stroke grippers and provides the added benefits of lighter weight, higher precision, and no maintenance. It is ideal for gripping larger items, including stacking boxes, gripping shaped parts, and keeping bags open. It has high repetition accuracy due to three rugged guide rods and a rack-and-pinion design.
The DHPL from Festo is a new generation of pneumatic long-stroke grippers that offers a host of advantages for high-load and high-torque applications. It is interchangeable with competitive long-stroke grippers and provides the added benefits of lighter weight, higher precision, and no maintenance. It is ideal for gripping larger items, including stacking boxes, gripping shaped parts, and keeping bags open. It has high repetition accuracy due to three rugged guide rods and a rack-and-pinion design.
Learn more.
Researchers successfully train a machine learning model in outer space for first time
For the first time, a project led by the University of Oxford has trained a machine learning model in outer space, on board a satellite. This achievement could revolutionize the capabilities of remote-sensing satellites by enabling real-time monitoring and decision-making for a range of applications.
Data collected by remote-sensing satellites is fundamental for many key activities, including aerial mapping, weather prediction, and monitoring deforestation. Currently, most satellites can only passively collect data, since they are not equipped to make decisions or detect changes. Instead, data has to be relayed to Earth to be processed, which typically takes several hours or even days. This limits the ability to identify and respond to rapidly emerging events, such as a natural disaster.
To overcome these restrictions, a group of researchers led by DPhil student Vit Ruzicka (Department of Computer Science, University of Oxford) took on the challenge of training the first machine learning program in outer space. During 2022, the team successfully pitched their idea to the Dashing through the Stars mission, which had issued an open call for project proposals to be carried out on board the ION SCV004 satellite, launched in January 2022. During the autumn of 2022, the team uplinked the code for the program to the satellite already in orbit.
The researchers trained a simple model to detect changes in cloud cover from aerial images directly on board the satellite, in contrast to training on the ground. The model was based on an approach called few-shot learning, which enables a model to learn the most important features to look for when it has only a few samples to train from. A key advantage is that the data can be compressed into smaller representations, making the model faster and more efficient.
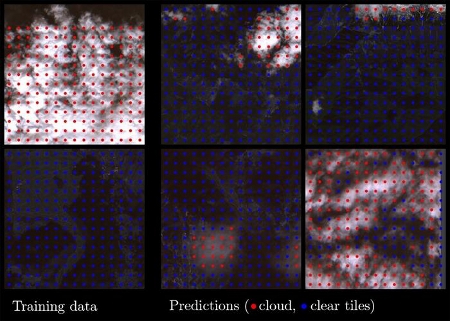
Illustration of the data used for training the tiny cloud classification model (left), and the predictions on new scenes (right). The entire training process took about 1.5 sec, including the time for encoding the entire training dataset, and 10 epochs of training a classification model. [Image credit: Sentinel-2 data (ESA) processed by Vit Ruzicka]
Ruzicka explained, "The model we developed, called RaVAEn, first compresses the large image files into vectors of 128 numbers. During the training phase, the model learns to keep only the informative values in this vector; the ones that relate to the change it is trying to detect (in this case, whether there is a cloud present or not). This results in extremely fast training due to having only a very small classification model to train."
While the first part of the model, to compress the newly seen images, was trained on the ground, the second part (which decided whether the image contained clouds or not) was trained directly on the satellite.
Normally, developing a machine learning model would require several rounds of training, using the power of a cluster of linked computers. In contrast, the team's tiny model completed the training phase (using over 1,300 images) in around 1.5 sec.
When the team tested the model's performance on novel data, it automatically detected whether a cloud was present or not in around a tenth of a second. This involved encoding and analyzing a scene equivalent to an area of about 4.8 x 4.8 km2 (equivalent to almost 450 football [soccer] pitches).
According to the researchers, the model could easily be adapted to carry out different tasks and to use other forms of data. Ruzicka added, "Having achieved this demonstration, we now intend to develop more advanced models that can automatically differentiate between changes of interest (for instance flooding, fires, and deforestation) and natural changes (such as natural changes in leaf color across the seasons). Another aim is to develop models for more complex data, including images from hyperspectral satellites. This could allow, for instance, the detection of methane leaks, and would have key implications for combatting climate change."
Performing machine learning in outer space could also help overcome the problem of on-board satellite sensors being affected by the harsh environmental conditions, so that they require regular calibration. "Our proposed system could be used in constellations of non-homogeneous satellites, where reliable information from one satellite can be applied to train the rest of the constellation," Ruzicka said. "This could be used, for instance, to recalibrate sensors that have degraded over time or experienced rapid changes in the environment."
Professor Andrew Markham, who supervised Ruzicka's DPhil research, said, "Machine learning has a huge potential for improving remote sensing -- the ability to push as much intelligence as possible into satellites will make space-based sensing increasingly autonomous. This would help to overcome the issues with the inherent delays between acquisition and action by allowing the satellite to learn from data on board. Vit's work serves as an interesting proof-of-principle."
This project was conducted in collaboration with the European Space Agency (ESA) Φ-lab via the Cognitive Cloud Computing in Space (3CS) campaign and the Trillium Technologies initiative Networked Intelligence in Space (NIO.space) and partners at D-Orbit and Unibap.
The work was presented at the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS) conference on July 21, 2023.
Source: University of Oxford
Published September 2023
Rate this article
View our terms of use and privacy policy

